










Project Target
0% Remaining
340,000
Trees Planted out of 340,000 Trees
Project Location:
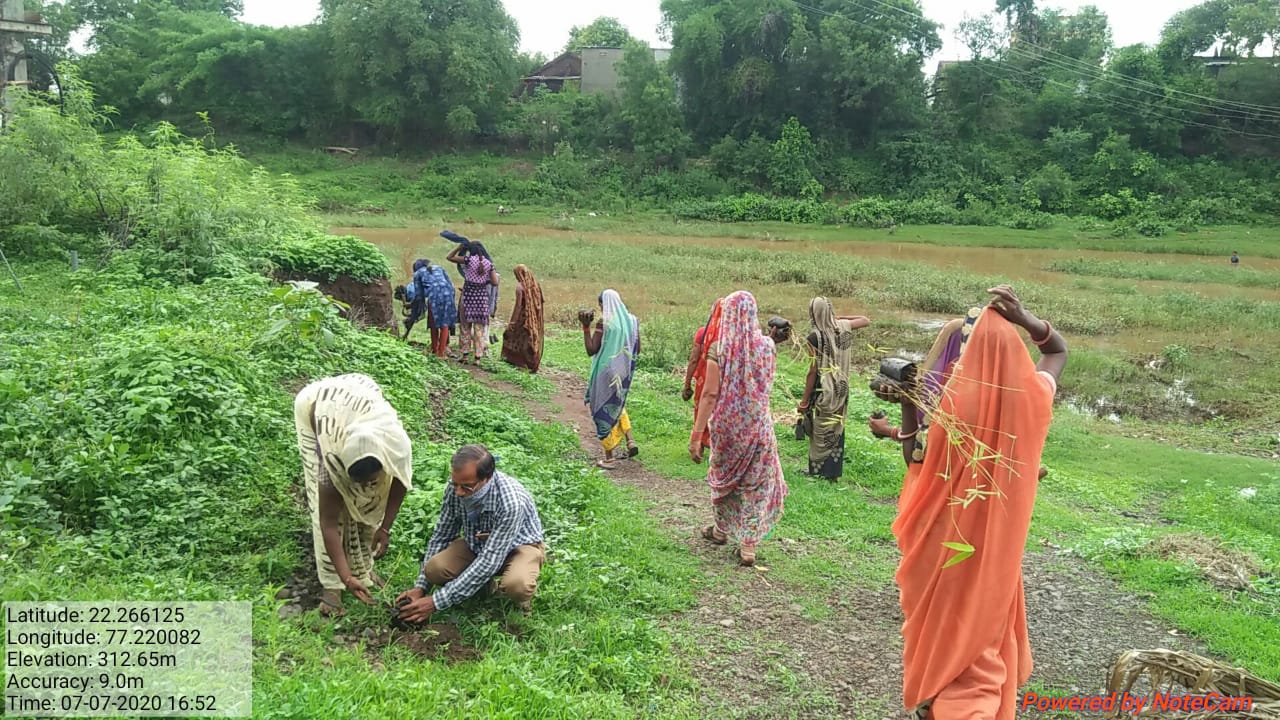
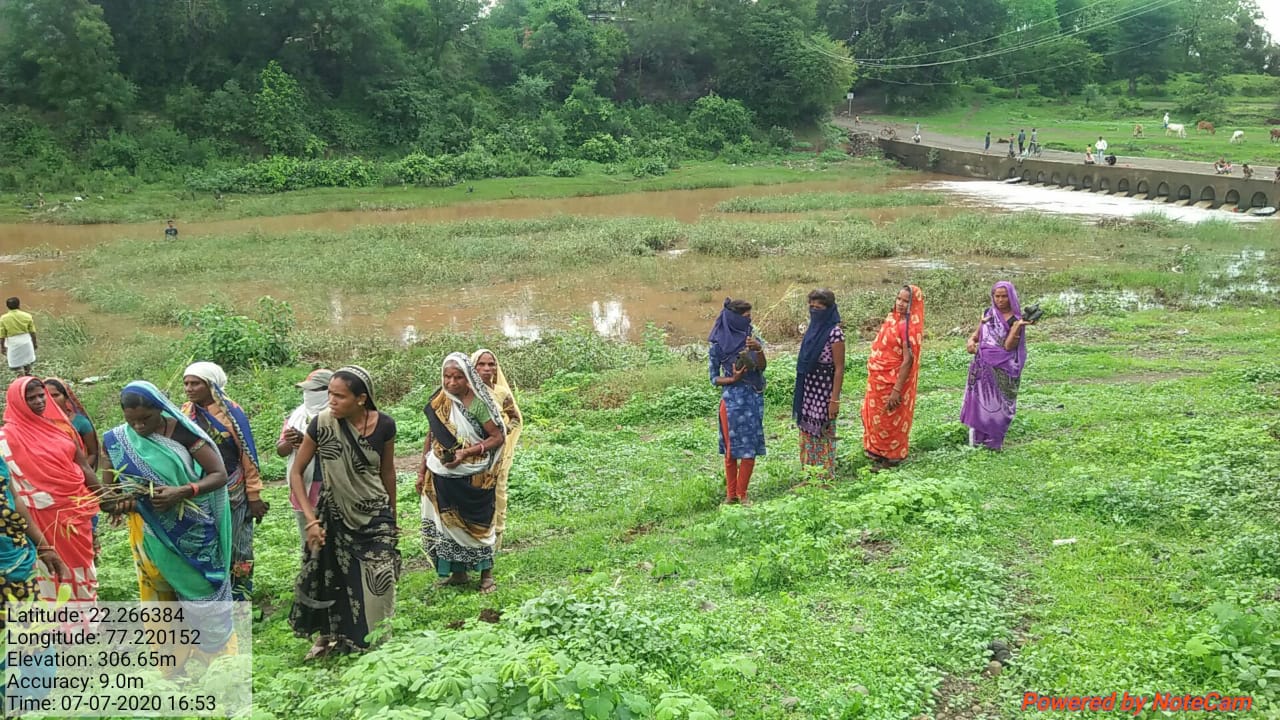
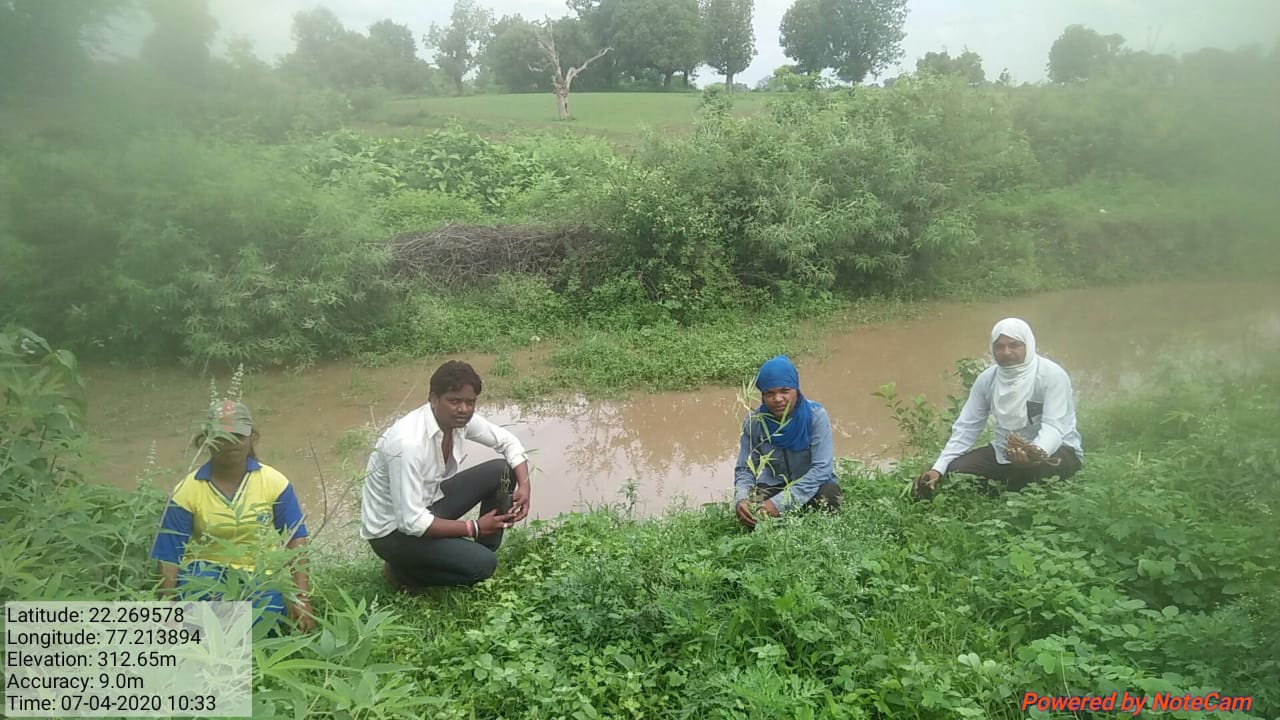
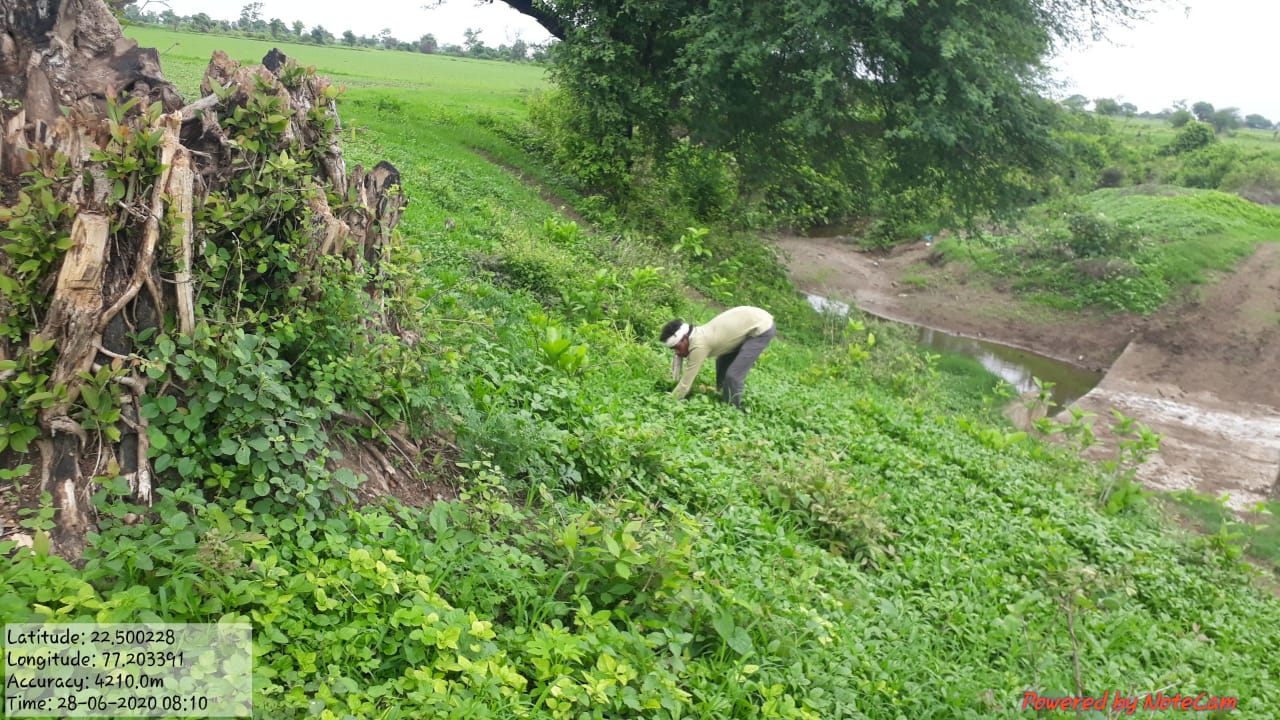
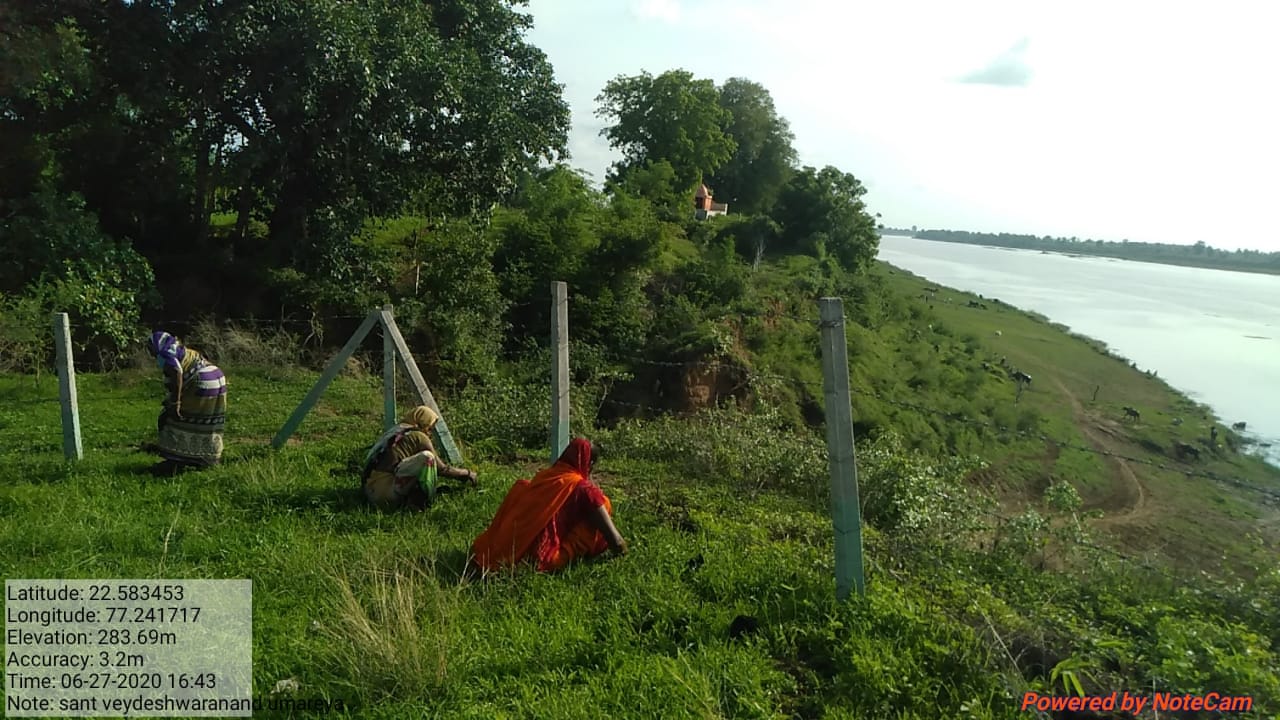
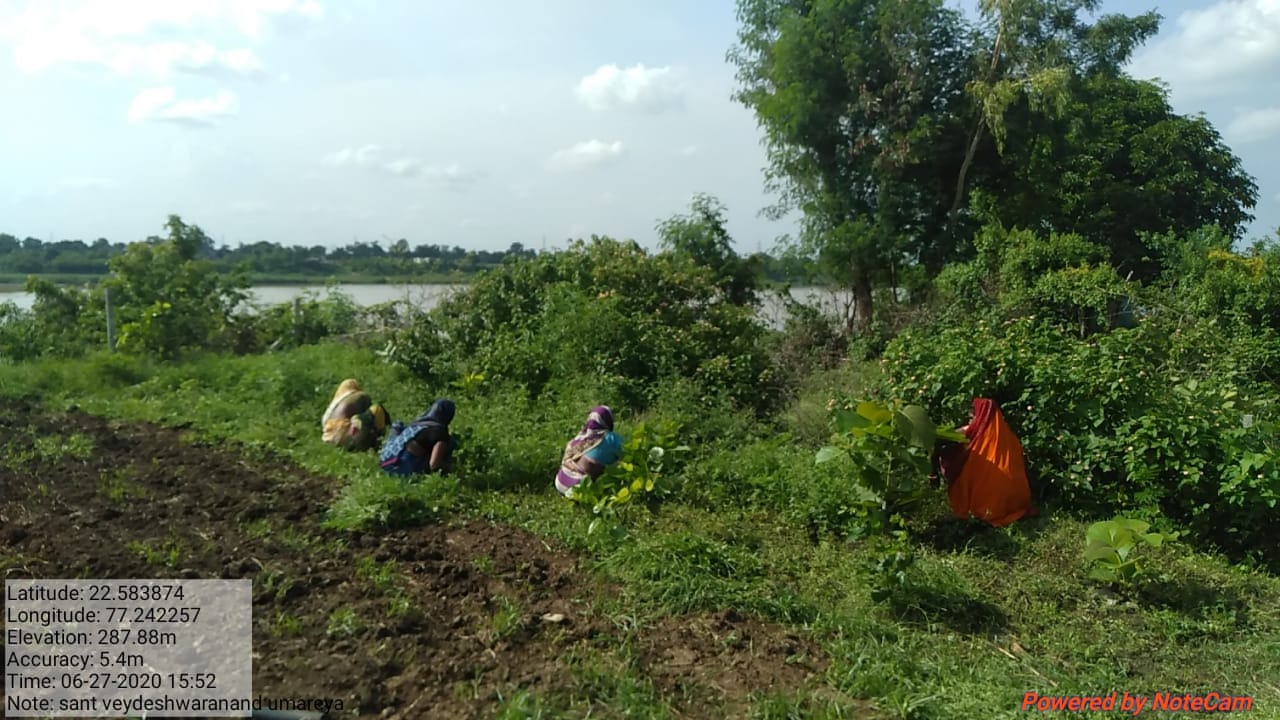
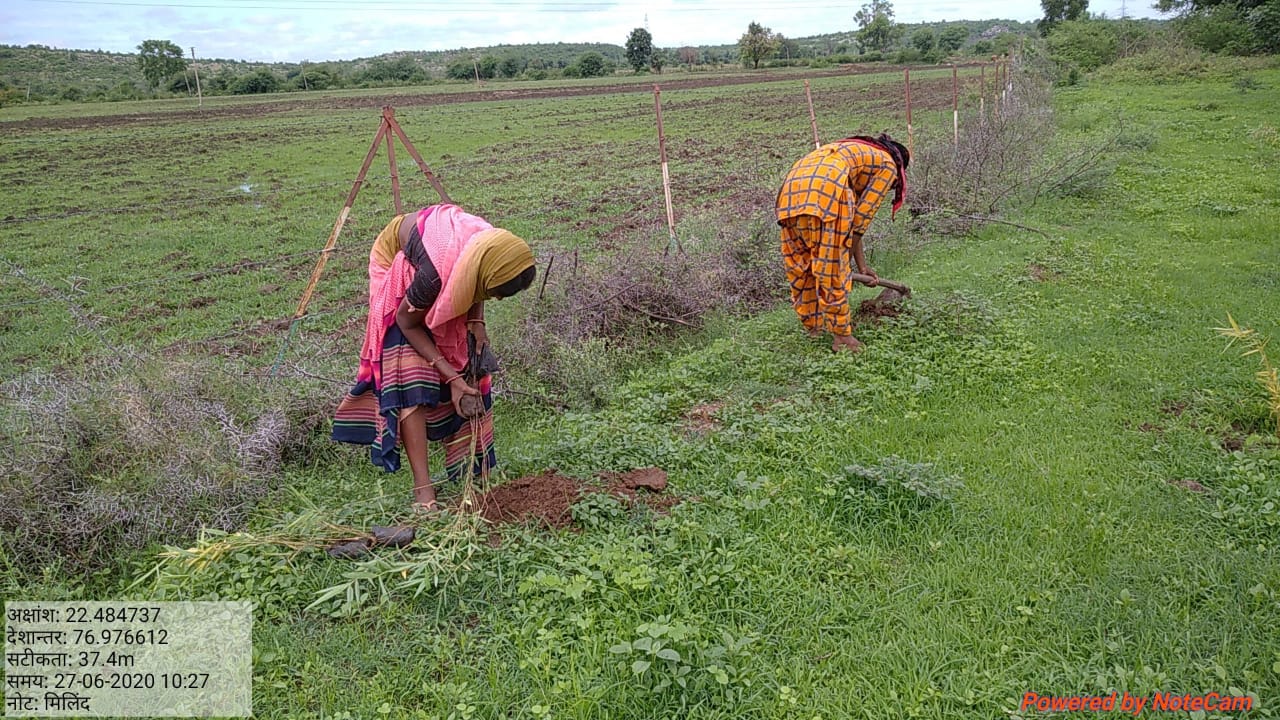
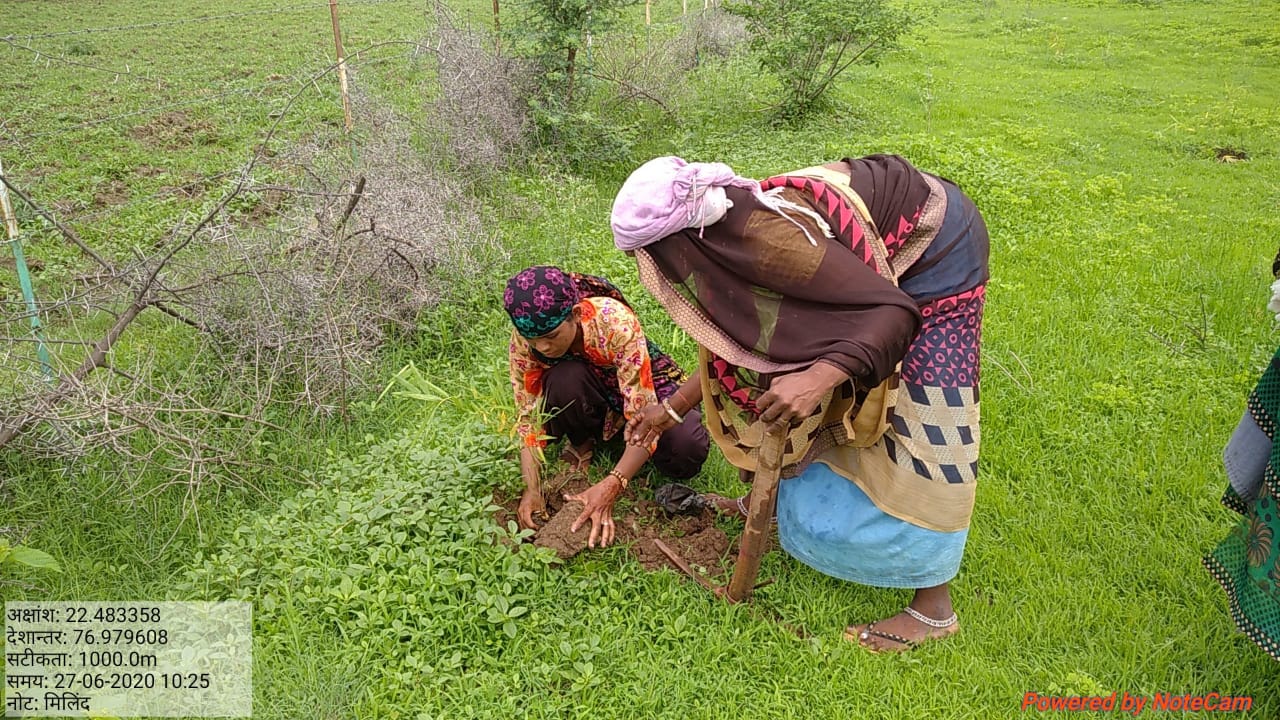
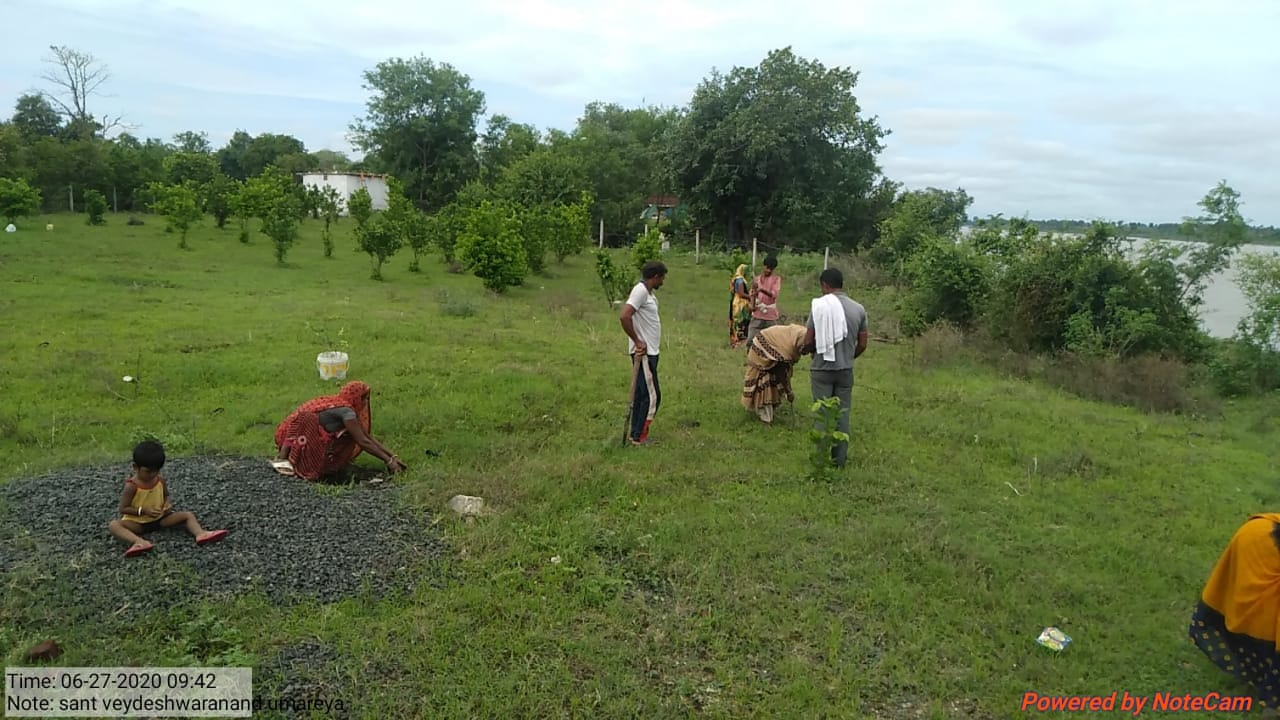
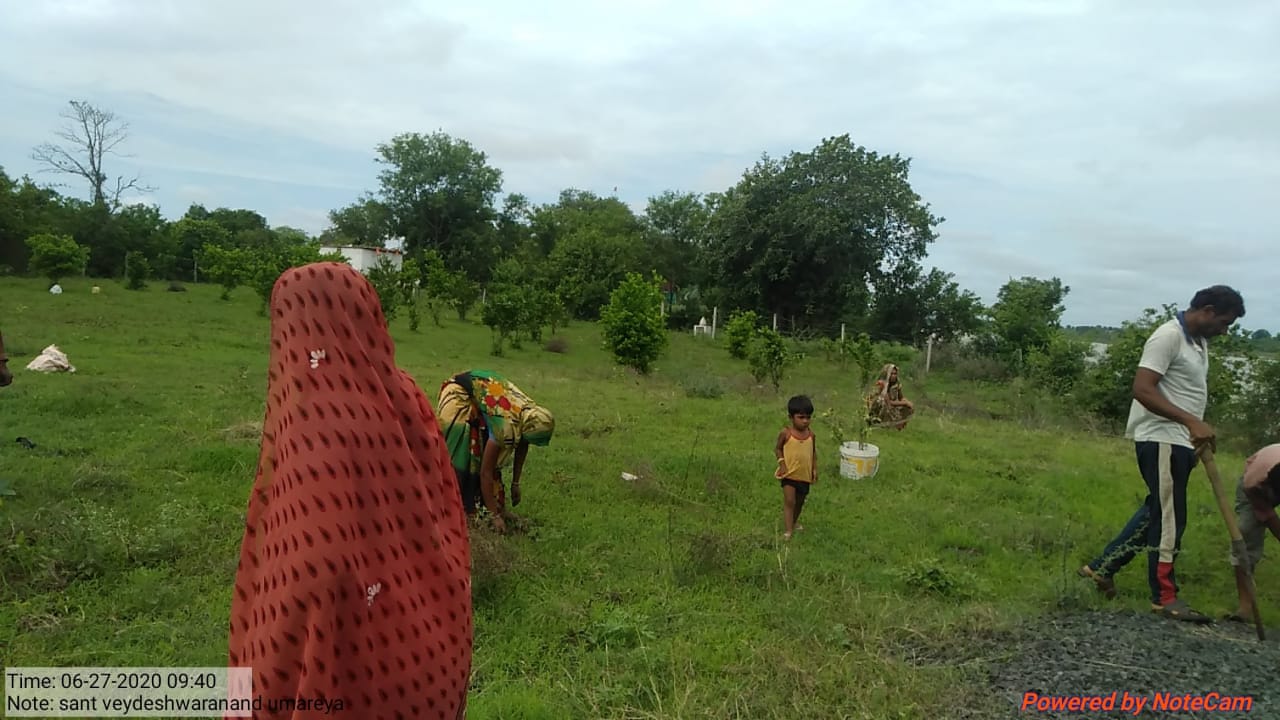
The plantation project is implemented in the Harda district covering village ranges of Manoharpura, Hirapur, Lachhora, Rahatakhurd, Kukrawad, Mahendragaon, and Kalkund adjoining to banks of the Narmada and its tributaries in Madhya Pradesh, India.
Project Aim
“Trees act as windbreaks and protect the valuable topsoil from erosion, which in turn retains the fertility of the soil, thereby, aiding in agriculture and providing with a good produce”, according to Clive David, University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point, College of Natural Resources. The State Government of Victoria stresses the contribution of trees in improving groundwater recharge. Soil erosion has long-term impacts as it causes loss of fertile topsoil and reduces the productive capacity of the land and thereby creating a risk to global food security (Patil et al. 2014). It is estimated that in India about 5334 million tonnes of soil is being detached annually due to various reasons (Narayan and Babu, 1983).
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) also mentions the importance of trees in contributing to the protection of soil and in improving its quality, leading to healthy crops and eventually ensuring food security. The Guardian mentions the importance of trees in pest control and soil nourishment. Thus, to improve the agricultural output as well as the overall environment of an area, trees are extremely important. The plantation near to the bank of Narmada watershed and tributaries would help to restore degraded land, increase carbon sequestration potential, improve soil infiltration capacity and limit soil erosion, soil moisture conservation, increase plant water uptake and reduce surface runoff, improve wildlife habitat and forest products in the area.
Teak (Tectona grandis) is a large, deciduous-tropical tree and is widely established throughout the tropics due to its multi-dimensional agro-environmental benefits. Plantation of teak is beneficial in the protection of water and soil resources by reducing bulk density, increasing the availability of nutrients, and producing and storing more organic material. Teak has the highest capacity for carbon sequestration among other trees in India. Because of its limited closure of the species canopy, teak enables farmers to diversify production, reduce farm risk, contribute to food security, and generate income opportunities.
Bamboo (Bambusa spp.) is a fast-growing species, having an average height of 20-30mtr and it grows best along riverbanks or valleys with fertile and moist soil. The plantation of Bamboo will function as a carbon sink, provide organic matter, and regulate water levels in watersheds. It is a sustainable resource because of its vegetation spread which allows the formation of forests much faster as compared to other tree species. Moreover, a bamboo plantation in and around crop fields creates a bio-fence which is helpful in tackling man-animal conflict. Unlike other types of commercial forestry crops where trees must be clear-cut and replanted, in bamboo plantations, only mature stems are harvested while younger stems are left untouched to mature and develop.
Teak (Tectona grandis) and Bamboo (Bambusa spp.), Mango (Mangifera indica), Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus), Guava (Psidium guajava), Neem (Azadirachta indica).
Plantation of local trees along the riverbanks could be the most effective restoration project enhancing the overall ecological health and ecosystem services. The trees planted will help reduce the risk of flooding, act as a security for the farmers’ crops, help conserve the soil and help to rejuvenate water table of the banks. Trees planted to provide shade, clean the soil and filter the water percolating through it by absorbing chemicals and other pollutants. Carbon management in forest plantation is the single most important agenda of our time in the context of the greenhouse gas effect and mitigation of climate change effects. Teak has the highest capacity for carbon sequestration among trees in India. Overall, upon maturity, each tree can absorb approximately 20kg of CO2 per year which is considered globally as a conservative estimate for sequestration potential of trees.
Bamboo is known to be one of the fastest-growing plants in the world. It can form a tightly woven mat of roots and rhizomes underground, which are effective in holding soil to strengthen agroforestry ground (Guillermo Tardio et al. 2017). The bamboo forest ecosystem is an integral part of the forest ecosystem and a prime source of carbon sink on earth. Bamboo can supplement in promoting alternative livelihood options regarding Bamboo-crafts to the two major tribal groups, Gond and Korku in the range. Additionally, as the bamboo grows in clumps, it creates a natural fence to control crop raiding by wild animals into the crop fields.
| Name of the Company | Number of Trees | Fiscal Year |
|---|---|---|
| Dun & Bradstreet India | 16,600 | 2021-22 |
| HDFC Bank Ltd. | 150,000 | 2020-21 |
| Merck Ltd. | 40,000 | 2018-19 |
| SBI Life Insurance | 50,000 | 2016-17 |
Social Impact of Growing Trees
Community Engagement
Tree planting initiatives often involve local communities, which can lead to greater community cohesion.
Ecological Education
Provides opportunities for community members, especially children, about the importance of environmental sustainability.
Urban Beautification
Trees contribute to the aesthetic enhancement of urban areas, making cities more pleasant and liveable.
Climate Resilience
By improving green cover, tree planting helps make communities more resilient against climate impacts like heatwaves.
Employment Creation
Planting trees creates employment for local community members like planting and maintenance, administrative roles, and more long-term jobs in management.
Wildlife Habitat
Trees provide critical habitats for various species of wildlife. Enhancing tree cover helps preserve biodiversity, which can be an ecological boon for local communities
Copyrights @ 2025 All rights reserved by Pangea EcoNetAssets Pvt Ltd.